Indications:
- Pulmonary (lung) hyperinflation (or pulmonary insufflation, or alveolar recruitment, or pulmonary volume recruitment, or pulmonary volume augmentation) is a technique that helps a child increase their lung volume by the insufflation of air to the lungs using a modified ventilatory bag.
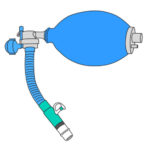
- This technique can be used regularly to prevent complications from retained secretions and also to treat pulmonary infections.
- The steps in the method below may serve as a guide; speak to your healthcare team about the specific equipment that your child uses.
Considerations:
- Pulmonary hyperinflation provides the child with a volume of air large enough to produce an effective cough that will in turn help clear secretions.
- This technique is possible in ventilated and non-ventilated children.
- This technique is rarely used on children with a tracheostomy. If this is the case with your child, consult the healthcare team for specific instructions.
- Based on your child’s condition and the results of tests (pulmonary function tests), your healthcare team can recommend the use of this technique alone or with expiratory aid techniques used simultaneously to help your child cough better.
- Good handwashing is essential before and after providing care to your child.
- Ensure the comfort of your child during care by using different positioning techniques and distraction techniques.
Frequency:
- 3 to 5 maneuvers per session (1 maneuver = 1 inspiration with bag/1 expiration/1 abdominal thrust or 1 thoracic compression), if appropriate.
- If the secretions are not sufficiently cleared: 5 to 8 maneuvers or until your child clears their secretions with an effective cough.
- 2 to 4 sessions per day regularly or more if needed, according to your child’s healthcare team.
- It is suggested that each session not last more than 10 minutes in order to avoid hyperventilation and dizziness.
- It is suggested that you wait 10 minutes between each session.
- Apply the technique before meals or at least 2 hours after a meal in order to avoid stomach discomfort and vomiting.
Required materials:
Refer to your healthcare team if the material used or the sequence of steps taught is different from what is described in the method of care.








